Having sleepless nights, here is how it will affect your day
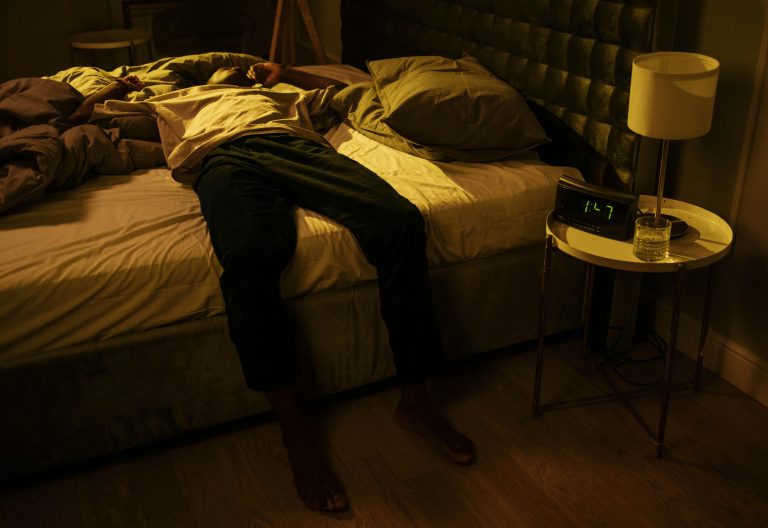

Sleep deprivation happens when a person does not get enough sleep, thereby straining to sustain their day-to-day lives and health. It is recommended that people get up to eight hours of sleep.
However, it is common for people to sacrifice their sleep for work, school, or fun, but even one night of inadequate sleep can leave people feeling tired, less productive and more prone to mistakes the next day.
As sleep debt grows over time, it begins to take a toll on your mental and physical health. It might also increase your risk of certain cancers, diabetes, and even car accidents, while also reducing your quality of life.
Here is what happens to your body when you don’t log enough hours under the covers.
1. Can cause hypertension
Getting less than five hours of sleep per night has been linked to an elevated instance of hypertension. This is because sleep helps our bodies regulate hormones that cause stress, and lack of rest can amplify the effects of stress on the body.
Long-term sleep deprivation has been associated with increased blood pressure, higher heart rate and inflammation.
All of this puts unnecessary strain on your heart and can lead to hypertension.
2. Reduces your concentration and focus
If you spend few hours sleeping, you’re likely to struggle to stay alert and productive in class, at work, or while doing chores, thereby causing you problems at work, school and even in relationships.
Not only can missed sleep make you more forgetful, but there’s also a growing body of research indicating that sleep has an impact on learning and memory.
Researchers suggest that sleep is critical to the process of consolidating the things we learn in the brain.
In other words, we need proper rest to lock in new information and commit it to memory.
3. Leads to irritability and mood swings
Lack of sleep makes people short-tempered, impatient and emotionally unstable because it makes a person feel more anxious or depressed.
Without enough sleep, people tend to feel irritable, frustrated and unmotivated.
They may also struggle to deal with change and regulate their emotions.
4. Weakens the immune system
Like the rest of our body, the immune system performs better when we get adequate sleep.
A prolonged lack of sleep causes a similar reaction to high levels of stress; it can decrease your antibody response and make you more vulnerable to illnesses like colds, flu, and infections.
Sleep is important for maintaining a healthy immune system and its deprivation can weaken the immune function.
Poor sleep can compromise the immune system, making athletes more susceptible to illnesses and injuries.
5. Causes memory problems
After just one unrestful night, we have all experienced mental fog, fatigue, short temper and lack of focus. When the brain is not able to rest enough over a longer period of time, mental faculties can decrease drastically.
We know that adequate sleep is necessary for people to feel sharp, concentrate and learn, but it also impacts our problem-solving skills and the ability to regulate our emotions and make decisions.
Sleep-deprived people also have problems with balance, reflexes and motor skills; as a result, they are much more likely to injure themselves.
Many scientists believe that sleep is important for giving the brain time to organise itself and, specifically, to commit information from short-term memory to long-term memory.
Adequate sleep is crucial for memory recall.
6. Makes you hungrier, weighty
Another impact of lack of continual sleep is rapid weight gain occasioned by excessive eating.
Lack of sleep is related to higher amounts of cortisol, a stress hormone that causes anxiety, stress and frustration, which often contribute to emotional eating and poor nutritional habits.
Another hormone called ghrelin, which is produced in the stomach, can actually make people feel hungrier.
Over time, sleep deprivation negatively impacts the body’s metabolism and eating habits.
Tiredness often leads to unhealthy cravings and overindulgence, accompanied by a decrease in stamina and physical activity.
Research has shown that people who feel unrested are more likely to choose foods that are rich in carbohydrates and sugar.
Science shows that a decrease in exercise, combined with an increase in the amount of food eaten, plus an increase in the caloric value of the food ingested, equals weight gain.
Obesity is a known risk factor for insomniacs.
7. Affects your skin, causes ageing
Less sleeping hours is likely to cause dull skin, puffy eyes, and premature ageing signs like wrinkles.
These impacts often lead to weakened skin barrier function, increased transepidermal water loss (TEWL), decreased skin elasticity and accelerated ageing.
It can also contribute to dark circles, dullness, and increased inflammation, potentially exacerbating existing skin conditions.
8. Leads to poor decision-making
Sleep deprivation affects judgment, making people take risky or careless decisions.
This problem significantly impairs one’s decision-making by affecting cognitive functions like attention, concentration, and impulse control.
Reduced sleep can also lead to increased risk-taking, impaired judgment, and difficulty processing information, all of which contribute to poor decision-making.
9. Reduces your physical performance
Body strength, stamina, and coordination decline are the possible results of sleep deprivation since it affects a person’s physical performance by reducing their stamina and increasing exhaustion, thereby reducing reaction time and accuracy, thereby affecting the body’s ability to resynthesise energy during exercise.
Athletes may experience slower reactions and reduced accuracy in tasks requiring quick reflexes and precision.
Sleep deprivation also affects the body’s ability to store and utilise energy. It can reduce muscle and liver glycogen, impacting the reintegration of energy substances needed during exercise.
Due to all these impacts, a person’s mental health is likely to be affected, which can then lead to a distorted perception of fatigue.
10. Worsens your stress and anxiety levels
Tiredness increases stress hormone levels, making small problems feel overwhelming.
Anxiety is frequently connected to sleeping problems.
Excess worry and fear make it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep through the night.
Sleep deprivation can worsen anxiety, spurring a negative cycle involving insomnia and anxiety disorders.
Anxiety and panic attacks can also be a common reaction for people struggling with chronic sleep deficiency; they have been shown to have a lower tolerance for even mild daily stressors.
Like depression, sometimes it can be difficult to understand what came first: anxiety or a sleep disorder.